Action for SDGs
Working on SDGs
Click here Achievements!!
Annual CO2 emission reduction-----671t CO2/年
Annual Power Production ----1211 MWh/年
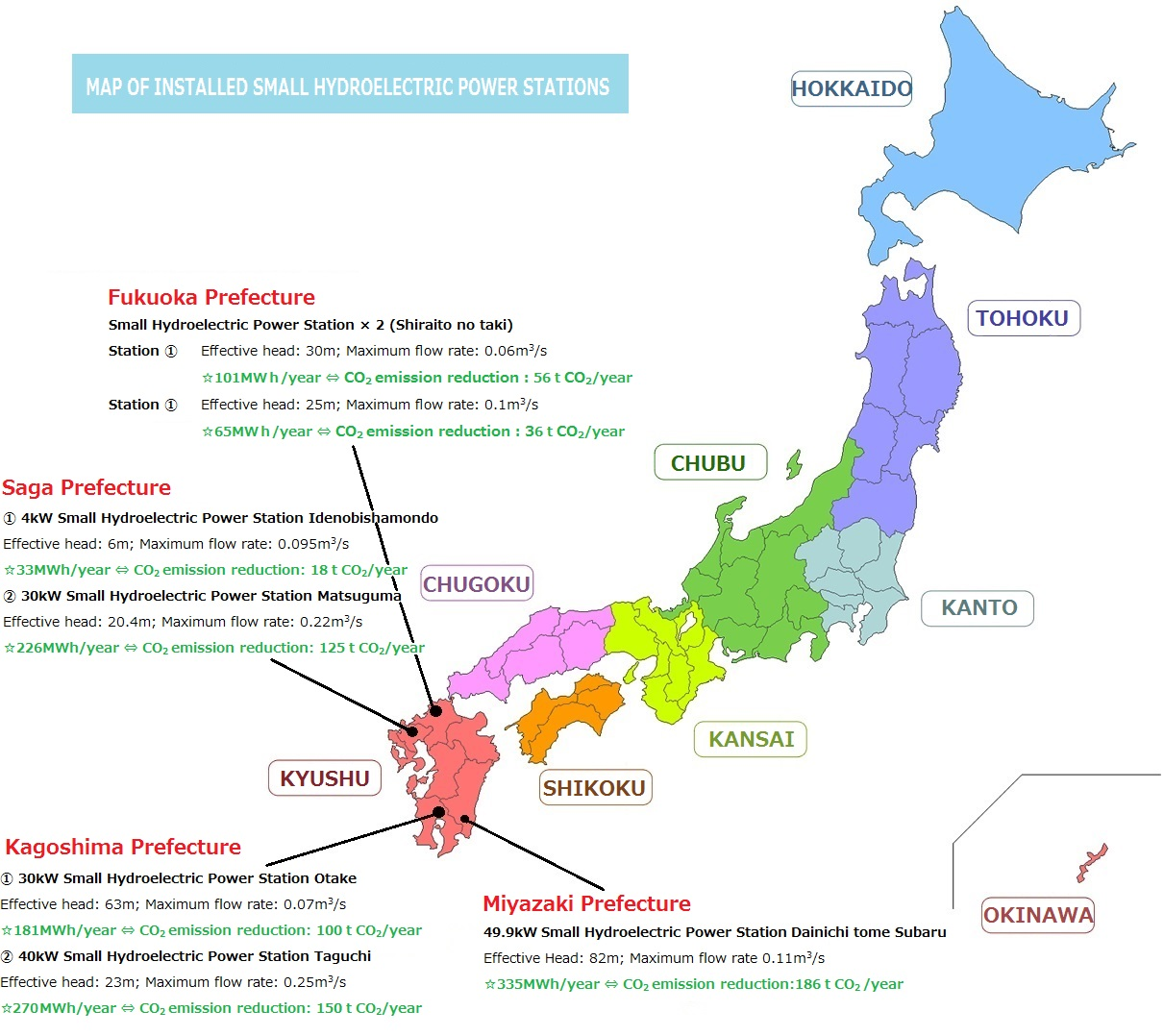
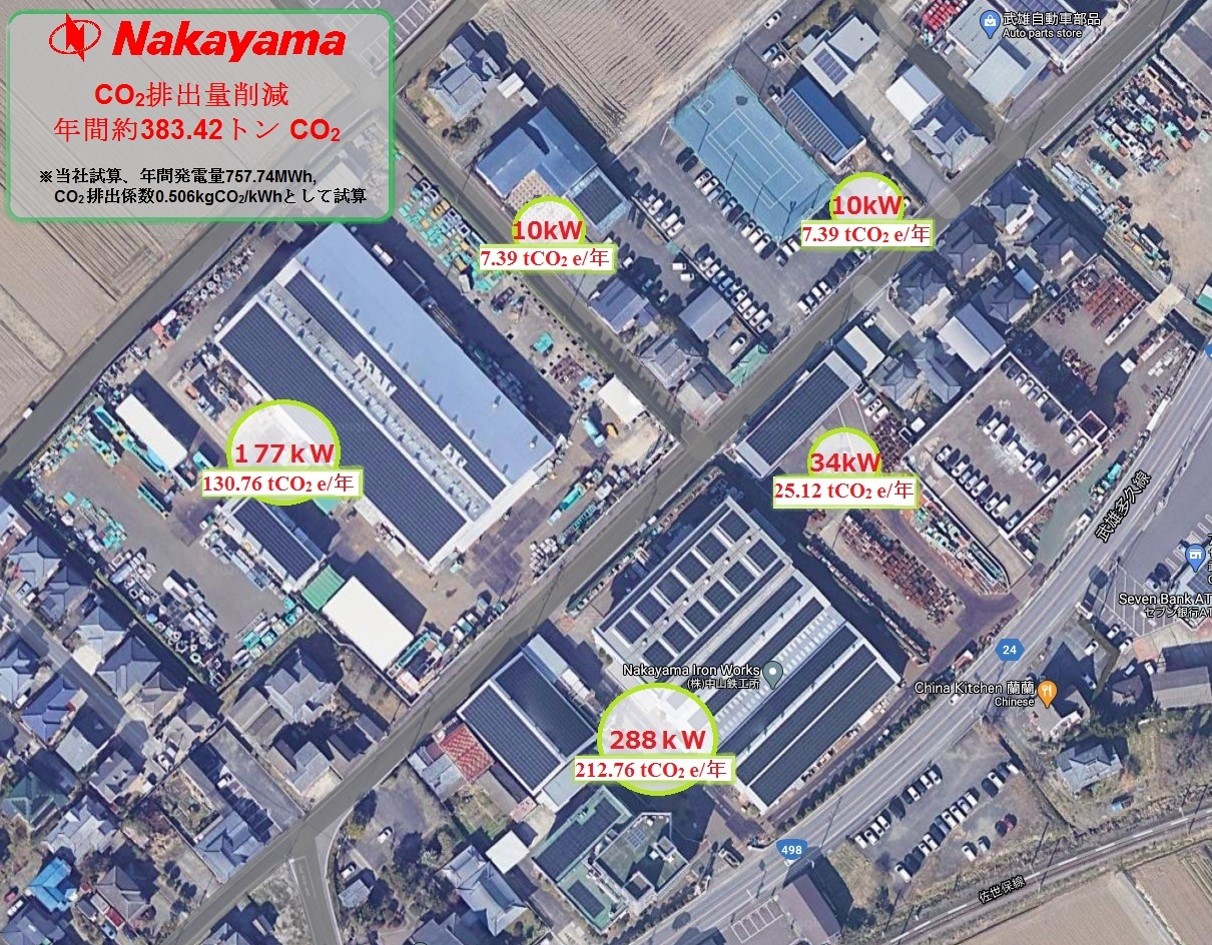
Click here Achievements!!
Annual CO2 emission reduction-----383t CO2/年
Annual Power Production ------757 MWh/年
Nakayama started to work on SDGs
The SDGs mean 17 goals to be achieved by 2030 set by the United Nations general assembly held in September 2015 for the future of mankind and the earth.
A lot of corporations are more and more expected to help achieve the goals which will be globally applied in the world.
Nakayama has determined to promote and achieve the SDGs through the daily business operation.

For details of SDGs, kindly refer to “JAPAN SDGs Action Platform, Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
Major activities
Contribution to SDGs through recycling of construction wastes
1.The re-use of concrete and asphalt wastes becomes possible.
2.Classification of construction wastes
3.Development of recycling crushers which are environmentally friendly.
4.Activities eliminating the dangerous work environment using IoT and AI
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Contribution to SDGs through small-scale power generation by the natural energy
1.Supporting power supply to non-electrified areas.
2.Working on SOFC (Solid Oxide Fuel Cells)
3.Working together with domestic and overseas universities
![]()
![]()
Activity examples

Development of small-scale power generation
Nakayama Iron Works, Ltd. has been studying and developing the small-scale power generation system as a
renewable source of energy
Targets
| 7.1 | By 2030, ensure universal access to affordable, reliable and modern energy services. |
|---|---|
| 7.2 | By 2030, increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. |
| 7.3 | By 2030, double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency. |
| 7.a | By 2030, enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology, including renewable energy, energy efficiency and advanced and cleaner fossil-fuel technology, and promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology. |
| 7.b | By 2030, expand infrastructure and upgrade technology for supplying modern and sustainable energy services for all in developing countries, in particular least developed countries, small island developing States, and land-locked developing countries, in accordance with their respective programmes of support. |

Work style reforms
We will work on the enhancement of benefits and flexible working time setting.
Targets
| 8.1 | Sustain per capita economic growth in accordance with national circumstances and, in particular, at least 7 per cent gross domestic product growth per annum in the least developed countries. |
|---|---|
| 8.2 | Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation, including through a focus on high-value added and labour-intensive sectors. |
| 8.3 | Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, decent job creation, entrepreneurship, creativity and innovation, and encourage the formalization and growth of micro-, small- and medium-sized enterprises, including through access to financial services. |
| 8.4 | Improve progressively, through 2030, global resource efficiency in consumption and production and endeavour to decouple economic growth from environmental degradation, in accordance with the 10-year framework of programmes on sustainable consumption and production, with developed countries taking the lead. |
| 8.5 | By 2030, achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all women and men, including for young people and persons with disabilities, and equal pay for work of equal value. |
| 8.6 | By 2020, substantially reduce the proportion of youth not in employment, education or training. |
| 8.7 | Take immediate and effective measures to eradicate forced labour, end modern slavery and human trafficking and secure the prohibition and elimination of the worst forms of child labour, including recruitment and use of child soldiers, and by 2025 end child labour in all its forms. |
| 8.8 | Protect labour rights and promote safe and secure working environments for all workers, including migrant workers, in particular women migrants, and those in precarious employment. |
| 8.9 | By 2030, devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products. |
| 8.10 | Strengthen the capacity of domestic financial institutions to encourage and expand access to banking, insurance and financial services for all. |
| 8.a | Increase Aid for Trade support for developing countries, in particular least developed countries, including through the Enhanced Integrated Framework for Trade-Related Technical Assistance to Least Developed Countries. |
| 8.b | By 2020, develop and operationalize a global strategy for youth employment and implement the Global Jobs Pact of the International Labour Organization. |

As a crusher manufacturer,
We is trying to reduce the emission of carbon by developing electric-driven crushers, enabling the choice of
alternative powers; either generator or commercial power supply.
Furthermore, the increase of construction wastes recycling facilities will help preserve the natural sand resources. Thus, we can contribute to the preservation of nature and biological diversity
Targets
| 9.1 | Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure, including regional and transborder infrastructure, to support economic development and human well-being, with a focus on affordable and equitable access for all. |
|---|---|
| 9.2 | Promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and, by 2030, significantly raise industry’s share of employment and gross domestic product, in line with national circumstances, and double its share in least developed countries. |
| 9.3 | Increase the access of small-scale industrial and other enterprises, in particular in developing countries, to financial services, including affordable credit, and their integration into value chains and markets. |
| 9.4 | By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes, with all countries taking action in accordance with their respective capabilities. |
| 9.5 | Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors in all countries, in particular developing countries, including, by 2030, encouraging innovation and substantially increasing the number of research and development workers per 1 million people and public and private research and development spending. |
| 9.a | Facilitate sustainable and resilient infrastructure development in developing countries through enhanced financial, technological and technical support to African countries, least developed countries, landlocked developing countries and small island developing States 18. |
| 9.b | Support domestic technology development, research and innovation in developing countries, including by ensuring a conducive policy environment for, inter alia, industrial diversification and value addition to commodities. |
| 9.c | Significantly increase access to information and communications technology and strive to provide universal and affordable access to the Internet in least developed countries by 2020. |
Targets
| 12.1 | Implement the 10-year framework of programmes on sustainable consumption and production, all countries taking action, with developed countries taking the lead, taking into account the development and capabilities of developing countries. |
|---|---|
| 12.2 | By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. |
| 12.3 | By 2030, halve per capita global food waste at the retail and consumer levels and reduce food losses along production and supply chains, including post-harvest losses. |
| 12.4 | By 2020, achieve the environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes throughout their life cycle, in accordance with agreed international frameworks, and significantly reduce their release to air, water and soil in order to minimize their adverse impacts on human health and the environment. |
| 12.5 | By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse. |
| 12.6 | Encourage companies, especially large and transnational companies, to adopt sustainable practices and to integrate sustainability information into their reporting cycle. |
| 12.7 | Promote public procurement practices that are sustainable, in accordance with national policies and priorities 12.8 By 2030, ensure that people everywhere have the relevant information and awareness for sustainable development and lifestyles in harmony with nature. |
| 12.8 | By 2030, ensure that people everywhere have the relevant information and awareness for sustainable development and lifestyles in harmony with nature. |
| 12.a | Support developing countries to strengthen their scientific and technological capacity to move towards more sustainable patterns of consumption and production. |
| 12.b | Develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products. |
| 12.c | Rationalize inefficient fossil-fuel subsidies that encourage wasteful consumption by removing market distortions, in accordance with national circumstances, including by restructuring taxation and phasing out those harmful subsidies, where they exist, to reflect their environmental impacts, taking fully into account the specific needs and conditions of developing countries and minimizing the possible adverse impacts on their development in a manner that protects the poor and the affected communities. |
Targets
| 13.1 | Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries. |
|---|---|
| 13.2 | Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. |
| 13.3 | Improve education, awareness-raising and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction and early warning. |
| 13.a | Implement the commitment undertaken by developed-country parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change to a goal of mobilizing jointly $100 billion annually by 2020 from all sources to address the needs of developing countries in the context of meaningful mitigation actions and transparency on implementation and fully operationalize the Green Climate Fund through its capitalization as soon as possible. |
| 13.b | Promote mechanisms for raising capacity for effective climate change-related planning and management in least developed countries and small island developing States, including focusing on women, youth and local and marginalized communities. |
*Acknowledging that the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change is the primary international, intergovernmental forum for negotiating the global response to climate change.
Targets
| 15.1 | By 2020, ensure the conservation, restoration and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems and their services, in particular forests, wetlands, mountains and drylands, in line with obligations under international agreements. |
|---|---|
| 15.2 | By 2020, promote the implementation of sustainable management of all types of forests, halt deforestation, restore degraded forests and substantially increase afforestation and reforestation globally. |
| 15.3 | By 2030, combat desertification, restore degraded land and soil, including land affected by desertification, drought and floods, and strive to achieve a land degradation-neutral world. |
| 15.4 | By 2030, ensure the conservation of mountain ecosystems, including their biodiversity, in order to enhance their capacity to provide benefits that are essential for sustainable development. |
| 15.5 | Take urgent and significant action to reduce the degradation of natural habitats, halt the loss of biodiversity and, by 2020, protect and prevent the extinction of threatened species. |
| 15.6 | Promote fair and equitable sharing of the benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources and promote appropriate access to such resources, as internationally agreed. |
| 15.7 | Take urgent action to end poaching and trafficking of protected species of flora and fauna and address both demand and supply of illegal wildlife products. |
| 15.8 | By 2020, introduce measures to prevent the introduction and significantly reduce the impact of invasive alien species on land and water ecosystems and control or eradicate the priority species. |
| 15.9 | By 2020, integrate ecosystem and biodiversity values into national and local planning, development processes, poverty reduction strategies and accounts. |
| 15.a | Mobilize and significantly increase financial resources from all sources to conserve and sustainably use biodiversity and ecosystems. |
| 15.b | Mobilize significant resources from all sources and at all levels to finance sustainable forest management and provide adequate incentives to developing countries to advance such management, including for conservation and reforestation. |
| 15.c | Enhance global support for efforts to combat poaching and trafficking of protected species, including by increasing the capacity of local communities to pursue sustainable livelihood opportunities. |

Promotion of industrial – academic – government collaboration
For the sustainable development, we will vitalize the global partnership and work on the collaboration with domestic and overseas universities.
Targets
| Finance | |
|---|---|
| 17.1 | Strengthen domestic resource mobilization, including through international support to developing countries, to improve domestic capacity for tax and other revenue collection. |
| 17.2 | Developed countries to implement fully their official development assistance commitments, including the commitment by many developed countries to achieve the target of 0.7 per cent of ODA/GNI to developing countries and 0.15 to 0.20 per cent of ODA/GNI to least developed countries ODA providers are encouraged to consider setting a target to provide at least 0.20 per cent of ODA/GNI to least developed countries. |
| 17.3 | Mobilize additional financial resources for developing countries from multiple sources. |
| 17.4 | Assist developing countries in attaining long-term debt sustainability through coordinated policies aimed at fostering debt financing, debt relief and debt restructuring, as appropriate, and address the external debt of highly indebted poor countries to reduce debt distress. |
| 17.5 | Adopt and implement investment promotion regimes for least developed countries. |
| Technology | |
| 17.6 | Enhance North-South, South-South and triangular regional and international cooperation on and access to science, technology and innovation and enhance knowledge sharing on mutually agreed terms, including through improved coordination among existing mechanisms, in particular at the United Nations level, and through a global technology facilitation mechanism. |
| 17.7 | Promote the development, transfer, dissemination and diffusion of environmentally sound technologies to developing countries on favourable terms, including on concessional and preferential terms, as mutually agreed. |
| 17.8 | Fully operationalize the technology bank and science, technology and innovation capacity-building mechanism for least developed countries by 2017 and enhance the use of enabling technology, in particular information and communications technology. |
| Capacity building | |
| 17.9 | Enhance international support for implementing effective and targeted capacity-building in developing countries to support national plans to implement all the sustainable development goals, including through North-South, South-South and triangular cooperation. |
| Trade | |
| 17.10 | Promote a universal, rules-based, open, non-discriminatory and equitable multilateral trading system under the World Trade Organization, including through the conclusion of negotiations under its Doha Development Agenda. |
| 17.11 | Significantly increase the exports of developing countries, in particular with a view to doubling the least developed countries’ share of global exports by 2020. |
| 17.12 | Realize timely implementation of duty-free and quota-free market access on a lasting basis for all least developed countries, consistent with World Trade Organization decisions, including by ensuring that preferential rules of origin applicable to imports from least developed countries are transparent and simple, and contribute to facilitating market access. |
| Systemic issues | |
| Policy and institutional coherence | |
| 17.13 | Enhance global macroeconomic stability, including through policy coordination and policy coherence. |
| 17.14 | Enhance policy coherence for sustainable development. |
| 17.15 | Respect each country’s policy space and leadership to establish and implement policies for poverty eradication and sustainable development. |
| Multi-stakeholder partnerships | |
| 17.16 | Enhance the global partnership for sustainable development, complemented by multi-stakeholder partnerships that mobilize and share knowledge, expertise, technology and financial resources, to support the achievement of the sustainable development goals in all countries, in particular developing countries. |
| 17.17 | Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships, building on the experience and resourcing strategies of partnerships. |
| Data, monitoring and accountability | |
| 17.18 | By 2020, enhance capacity-building support to developing countries, including for least developed countries and small island developing States, to increase significantly the availability of high-quality, timely and reliable data disaggregated by income, gender, age, race, ethnicity, migratory status, disability, geographic location and other characteristics relevant in national contexts. |
| 17.19 | By 2030, build on existing initiatives to develop measurements of progress on sustainable development that complement gross domestic product, and support statistical capacity-building in developing countries. |